There is no doubt that the Honor V10 has good performance and is a very worthwhile phone to buy. But before the purchase, we have a question: how about its workmanship? Here, we disassemble an Honor V10 to explore its internal structure and workmanship.
Teardown is what we do! Follow us on Facebook for the latest repair news.

Power off the phone and remove the SIM card tray.
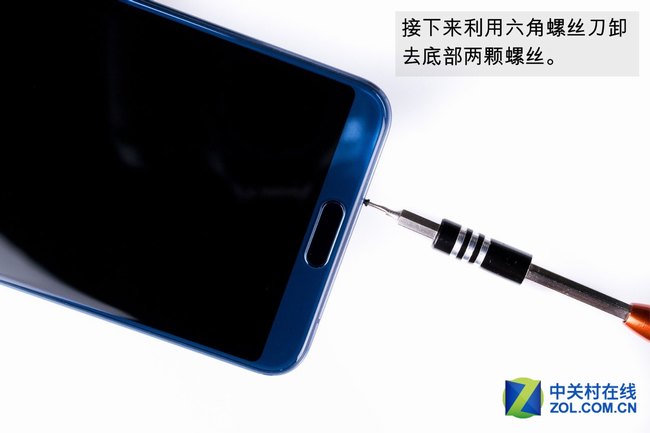

Then, use a hexagon screwdriver to remove the two screws at the bottom.

Use a pick to separate the back cover from the phone body.
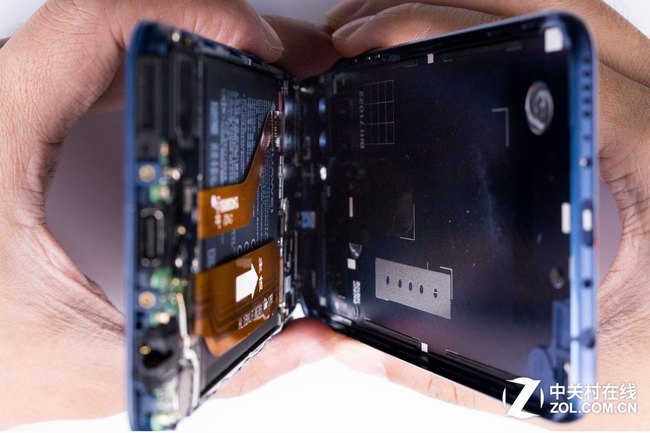

This is what we can see before separating the back cover from the body of the phone.

Since the fingerprint scanner is not designed on the back cover, the phone’s back cover can be successfully separated from the body. The edges of the phone are equipped with four thin sealing strips to prevent gaps between the body and the back cover.

The four corners of the back cover have been reinforced and thickened to prevent deformation caused by drops or impacts.

The back cover of the phone is coated with a layer of graphite thermal paste, which helps keep the motherboard running at a low temperature.

The back cover of the Honor V9 integrates multiple components. However, the design of the Honor V10 is exactly the opposite, as its back cover does not integrate any components.
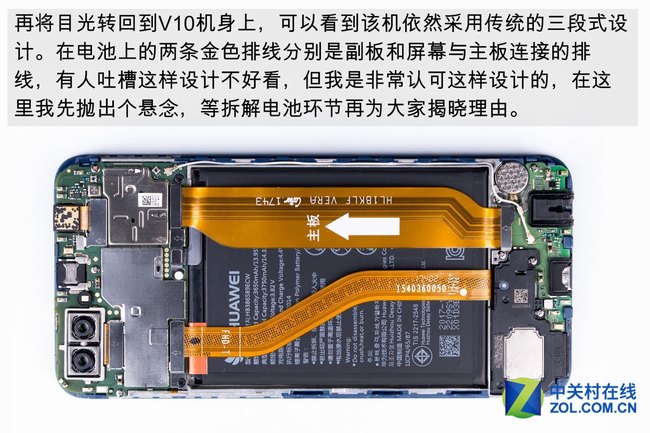
I believe that the full-screen design prompted the V10 to change its internal structure. To achieve a full-screen design, it is more convenient to integrate various sensors into the screen assembly.
Now, please take a look at the motherboard area. The V10’s motherboard has a very high space utilization. The metal cover secures all cable connectors in place to prevent component failures caused by connector dislodgement.

The port at the bottom has sealing material, which can prevent dust and water droplets from entering.

We will continue the teardown. First, remove the cover that secures the battery connector. The cover is secured by two screws.
Use an insulated pry bar to disconnect the power and PCB cables at the bottom.

Then, remove the three screws on the top of the motherboard.

Now, we can easily remove the motherboard from the body.
After removing the motherboard, the components at the bottom are clearly visible. The headphone jack is located at the top, while the light proximity sensor is built inside the body. The electronic vibrator is connected to the motherboard and is the only visible component. Additionally, the side buttons are also connected to the electronic vibrator.
Although the motherboard has good space utilization, it features a green color scheme.
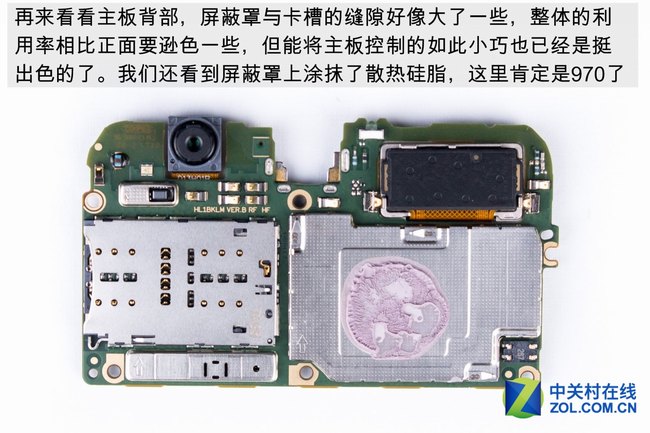
When looking at the back of the motherboard, the gap between the shield and the slot seems slightly large. Although its space utilization is lower than that of the front of the motherboard, designing a motherboard in such a small size is indeed not easy. The surface of the shield is covered with thermal grease.

Now, let’s separate the camera. The first metal cover on the camera connector has been removed, and the remaining two covers are connected to the base with metal clips. This design helps to reduce the space occupied on the motherboard.

The phone has a 16MP and 20MP dual-rear camera setup with an F/1.8 aperture. It does not support the OIS function.

We can see that the front camera has a large volume. The phone has a 13MP front camera with an F/2.0 aperture.
After removing the metal shield, there is still a layer of thermal grease. This is to prevent an air gap between the shield and the chip, as it would impede heat conduction.
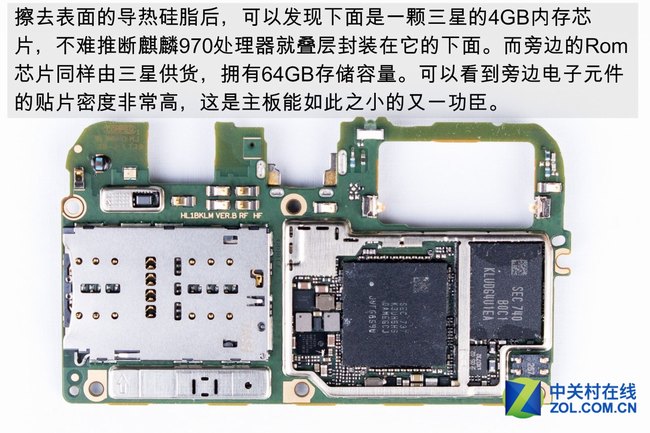
After wiping off the thermal grease on the surface, the 4GB memory chips are visible. The Kirin 970 processor is packaged under the chip. Samsung provides the storage chip and memory chip for this device.
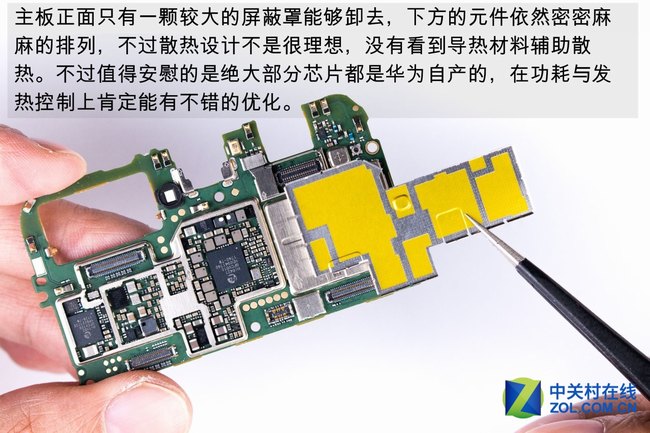
The front of the motherboard has only one large metal shield that can be removed. Under the metal shield, the component layout is dense, the heat dissipation design is poor, and there is no thermal material to assist in heat dissipation. Most of the chips are manufactured by Huawei and have been optimized for power consumption and heat control.
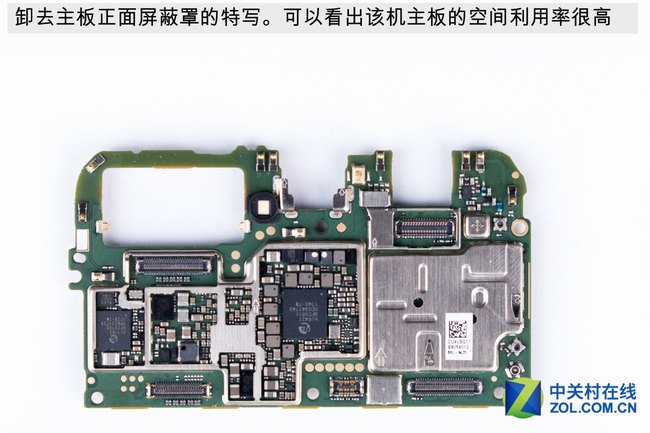
Close-up of the front of the motherboard. The space utilization of the motherboard is relatively high.

Use tweezers to remove the loudspeaker on the top.
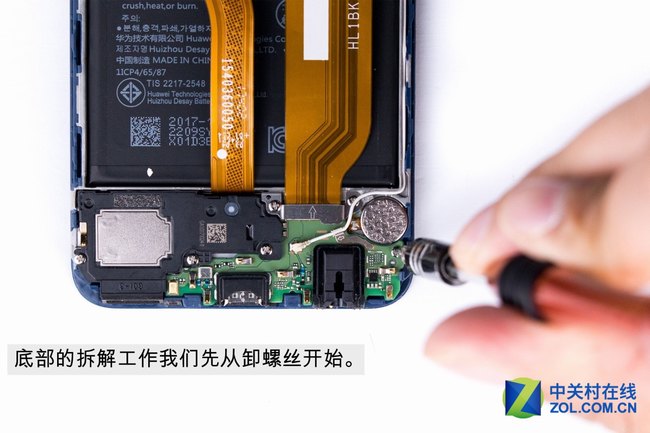

The disassembly process at the bottom begins with removing the screws.

Remove the loudspeaker. The surface of the loudspeaker doesn’t show its supplier.
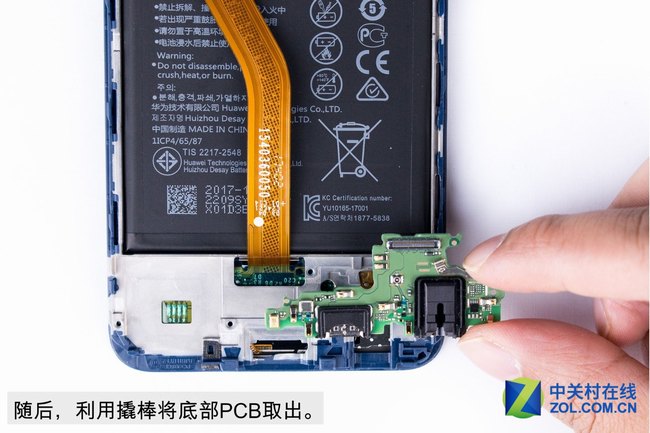

Next, use the pry tool to remove the PCB at the bottom.
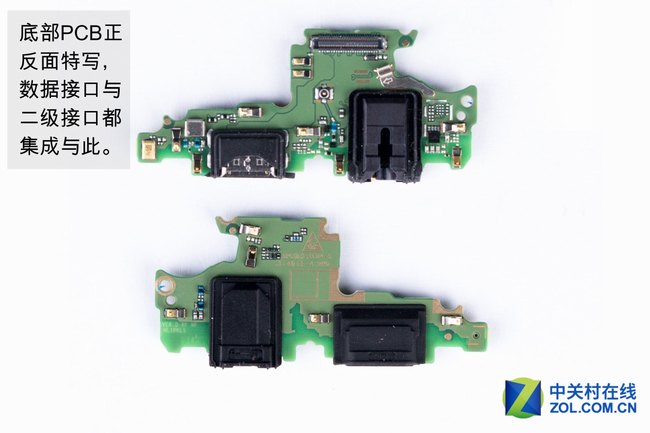
Close-up of the front and back of the PCB at the bottom. The data port and headphone jack have been integrated here.
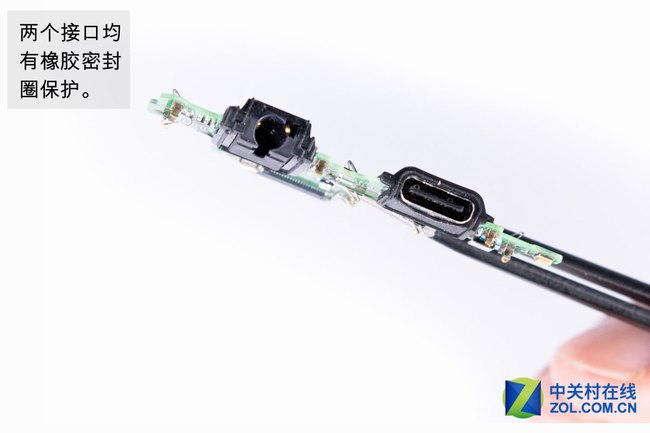
Both ports have been protected by rubber sealing.

The vibrator module is secured to the roll cage with glue and can be removed with tweezers.
As far as thickness is concerned, the vibrator is a rotor vibrator instead of a non-linear vibrator because the latter is usually thicker than the former.
After the components at the bottom are removed, the fingerprint reader cable is integrated into the screen assembly.

Although the battery is glued to the screen assembly, we were ultimately able to remove it successfully. The words on the battery indicate it has a typical capacity of 3750mAh, an energy density of 14.33Wh, and a rated voltage of 3.82V. Most Android phones have a rated voltage of 3.85V, but the 3.82V design will extend battery life.

A large number of double-sided tape marks are visible on the back of the battery. This battery is manufactured by Desay.

The Honor V10 with the Kirin 970 processor will undoubtedly deliver decent performance. After tearing it down, we found that the Honor V10 has excellent drop resistance, its ports are well protected, and it is very space-efficient.
Summary:
In general, the Honor V10 has excellent space utilization performance and good workmanship. The phone has an excellent sealing performance and good resistance to cracking.







Is there any way to extract the data inside if the motherboard is shocked? My phone was dropped into the water, and the motherboard short-circuited while trying to extract the data.