On December 21, Honor officially launched the Honor 9 Lite. The phone has four cameras and an impressive design. Now, let’s start tearing down the phone and exploring its internal layout and workmanship.
Teardown is what we do! Follow us on Facebook for the latest repair news.

Let’s start the teardown. First, power off the phone. Then, use a SIM card eject tool to remove the SIM card tray.
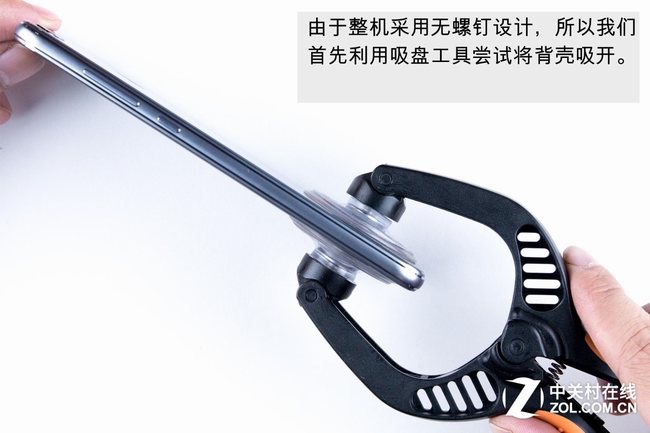

There are no screws on the bottom of the phone, so we will use a suction cup to remove the back cover.

After disconnecting the fingerprint cable on the back cover, we can remove it and explore the internal structure of the phone.

The internal structure of the phone adopts a three-segment design. The fingerprint cable on the back cover is connected to the mainboard and is hidden under the metal plate.

To disconnect the connector, we need to remove the three screws from the metal cover. Then, the back cover can be removed entirely.

The cover not only protects the fingerprint connector but also secures the two front camera connectors.
A green PCB on the back of the cover is used to connect the earphones and motherboard.

Disconnect the fingerprint cable. Since the battery flex cable has not yet been disconnected from the motherboard, a plastic insulating pry tool must be used to avoid short circuits.

Until now, the back cover has been successfully removed. We can see that it has been covered with sealing glue, providing excellent sealing performance.

After comparing the Honor 9 Lite with the Honor 9, we found that the Honor 9 uses more glue to secure the back cover. Obviously, the Honor 9 has better sealing.
The graphite cooling paste has been applied to the motherboard and the surroundings of the fingerprint module.

This phone features a three-segment design structure. The frame has been reinforced to withstand severe impacts. The battery surface is not covered by the flex cable, which is expected to be routed beneath the battery, making the disassembly process more difficult.

The chips on the motherboard are fully protected, and all connectors are secured with metal shields.

The next teardown step is to power off the system. First, remove all the screws securing the metal plate on the power connector.

The metal plate is secured by two screws. This metal plate protects the power connector, the sub-board connector, and the coaxial cable connector.

The display connector under the motherboard is secured by a metal plate. We will first remove the screws and then remove it.

A black rubber ring secures the detachable camera.

After removing two cameras from the rubber ring, we find that they are two independent modules. The left part is the 13MP sensor unit, and the right part is the 20MP sensor unit.

Later, I tried removing the metal plate on the primary camera but failed. So, I removed the motherboard from the phone body.

The 13MP primary camera on the right supports autofocus, while the one on the left is a 2MP camera. Both cameras are sealed together.
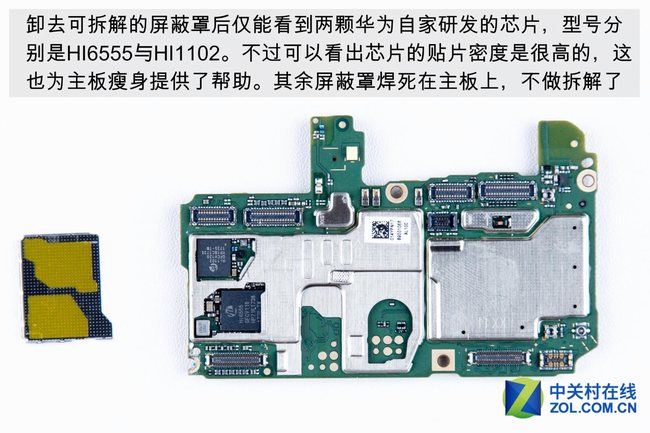
After removing the metal shield, only the HI6555 and HI1102 chips are visible. The other metal shield on the motherboard cannot be removed.
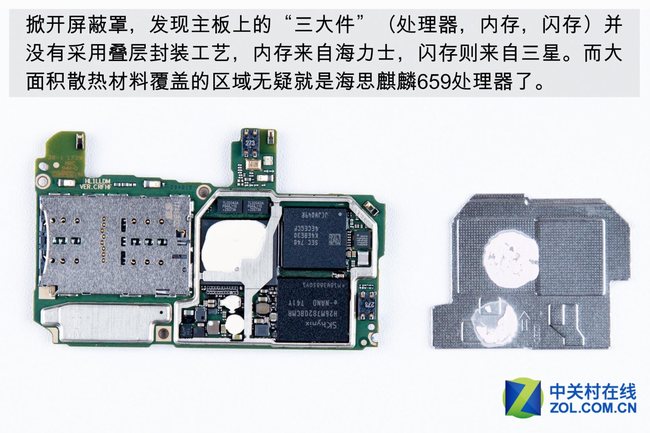
Remove the metal shield. We found three components on the motherboard, including the processor, memory chip, and flash chip. They do not use a multi-layer stacked packaging process. The memory comes from Hynix, while the flash is from Samsung. Undoubtedly, the area covered by the thermal paste is the Kirin 659 processor.
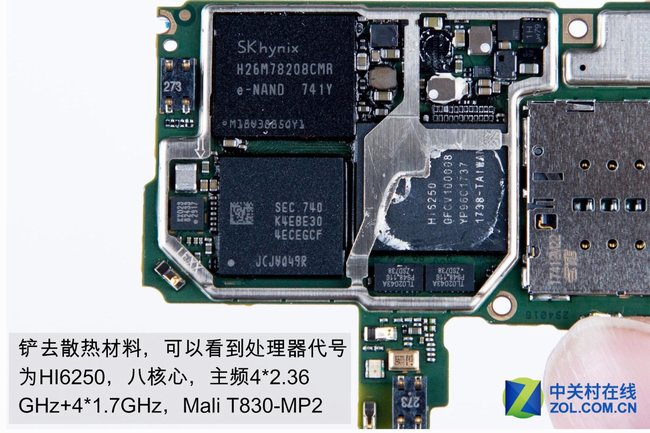
Remove the thermal paste. The processor model is HI6250, featuring a Mali T830-MP2 GPU. This chip consists of four cores clocked at up to 2.36 GHz and four cores clocked at up to 1.7 GHz.

Use tweezers to remove the headphones. However, this operation may damage the sealing foam at the bottom of the headset.

The light distance sensor is connected to the motherboard via metal contacts.

The teardown of components on the top is over. There are nine screws securing the bottom module.
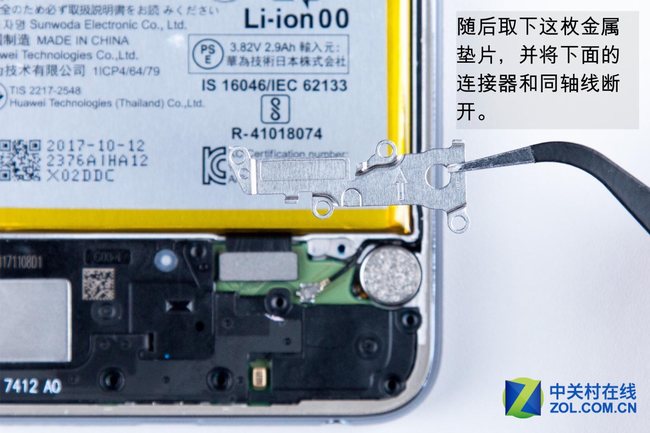

Next, take out the metallic gasket. Then, disconnect the connector and coaxial cable.
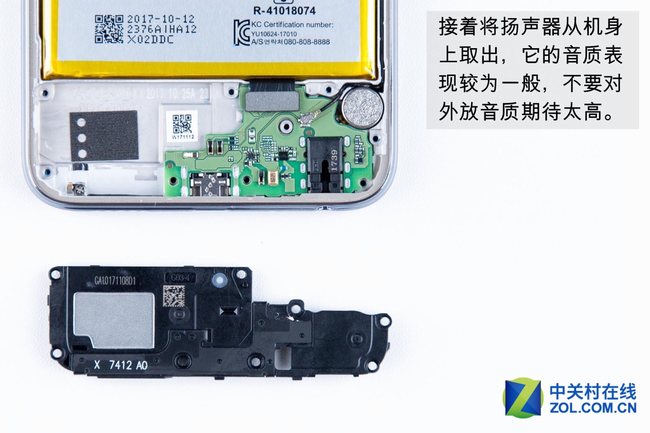
Remove the loudspeaker from the phone body. The loudspeaker has poor performance.
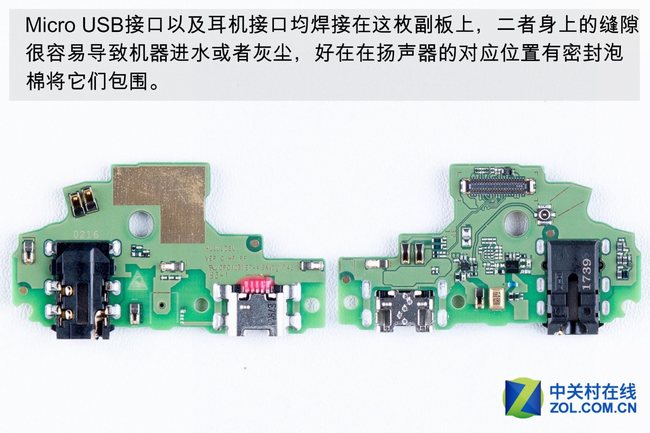
The micro USB port and the headphone port have been welded on the sub-board. The solder joints at these ports are prone to allowing water and dust to seep into the device.

The roll cage has been surrounded by foam. The vibrator is connected to the sub-board through metal contacts.

The thickness of this vibrator is 3.22 mm, and its diameter is relatively small. Therefore, this vibrator is likely a Z-type linear vibrator.

The battery has used a lot of glue, and it has become deformed because of the plentiful double-sided glue. The smartphone has a 3,000mAh battery.

The battery is provided by ATL, which is a leading battery manufacturer.

There are two cables under the battery. Do not damage them when removing the battery. Finally, we have completed the teardown of the Honor 9 Lite.
Summary:
Overall, the internal layout and craftsmanship of the Honor 9 Lite are not outstanding. However, the chip protection measures and port securing are satisfactory.

