USB 4 is a Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard released in September 2019. In the near future, most new laptops, computers, and devices will support USB 4.
In early September, the USB Promoter Group officially released the USB 4 specification, which means that the popularity of USB 4 has officially begun.
In March, Intel announced the opening of the Thunderbolt protocol to the USB Promoter Group, which significantly increased the transfer speed of USB 4. At the same time, this means that the most powerful data port, Thunderbolt 3, will be integrated directly into USB 4. In the future, devices using Thunderbolt 3 will not need to be licensed from Intel or pay high licensing fees, which will facilitate the development of port technology. This is very important.
Three characteristics of the USB 4 protocol
1. The USB 4 specification will introduce two-lane channels.
2. The transmission bandwidth reaches the 40 Gbps standard of Thunderbolt 3.
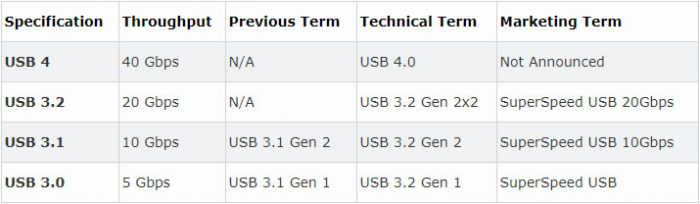
3. Backwards compatible with USB 3.2, 3.1, 3.0, 2.0, and Thunderbolt 3.
Combining the above three functions, USB 4 integrates the advanced technology of Thunderbolt 3, which offers a large bandwidth for data transfer, display input/output capabilities, and charging functions.
The full-featured USB 4 port is the most complete, smallest, and fastest physical port!
Additionally, USB 4 has been fully considered in terms of compatibility. It is directly compatible with USB 3.2, 3.1, 3.0, 2.0, Thunderbolt 3, and USB 4.
On the naming side, the USB Promoter Group will no longer use iterative naming schemes such as 3.0, 3.1, and 3.2. USB 4 may always use the USB 4 naming scheme. At the same time, its physical form will only be Type-C. Therefore, in the future, the USB port of electronic devices and related external expansion devices will adopt the Type-C, which will promote the development of laptops, tablets, and other devices to be lighter and thinner.
Why is USB 4 worth looking forward to?
In 2011, Thunderbolt, which was jointly developed by Intel and Apple and codenamed Light Peak, was officially announced. This is what we call the Thunderbolt port. Apple’s official website calls it a “lightning” port.
Since the Thunderbolt port combines the PCI Express and DisplayPort communication protocols, it is almost the only multi-function port that supports both high-speed data transmission and video/audio transmission before the full-featured Type-C standard was introduced. That is, it has USB, DP, HDMI, DVI, and VGA functions. And because it has a bandwidth of 10 Gbps in both directions, it can be considered a highly advanced port extension technology.
Thunderbolt 3 VS USB 4
Previously, there were two main reasons why the Thunderbolt 3 port was difficult to popularize: cost and hardware.
In terms of cost, using Thunderbolt 3 ports requires Intel licensing, and the licensing fee is high.
On the hardware side, the Thunderbolt 3 port needs an independent control chip, which is not cheap.
Under the obstruction of these two factors, the popularity of the Thunderbolt 3 port is difficult.
At the beginning of the year, Intel reached an agreement with the USB Promoter Group to solve the cost problem first. Future ports using the Thunderbolt 3 protocol will be completely free. Since then, Intel has integrated the Thunderbolt 3 controller directly into the processor from the 10th-generation Core processor, which solved the hardware issue. At the same time, with the help of the USB 4 specification, the Thunderbolt 3 port can be fully popularized, and Thunderbolt 3 can be accelerated to the consumer market.




ok best